Abstract
Background: The combination of doxorubicin, bleomycin, vinblastine and dacarbazine (ABVD) is one of the standard chemotherapy regimens for patients with classical Hodgkin lymphoma (cHL). However, a prominent limitation of this combination is the potentially life-threatening pulmonary toxicity associated with bleomycin. Brentuximab vedotin (BV) is an antibody-drug conjugate against the cell surface marker CD30 expressed on the malignant lymphocytes in cHL. The combination of AVD+BV has shown superior efficacy to ABVD regimen along with an acceptable safety profile in clinical trials. In this real-world study, we evaluated the effectiveness and safety of the AVD+BV regimen as frontline therapy in the treatment of cHL.
Methods: In this retrospective, single-center, real-world study, newly diagnosed advanced cHL patients aged >16 years were treated with frontline AVD+BV combination therapy from Jan 2019 to March 2022. The primary endpoint was complete response (CR) rate; the secondary endpoint was overall response rate (ORR; defined as CR + partial response, PR). Response and progression were evaluated at the end of every treatment course and during the follow-up period. Safety assessments were also done.
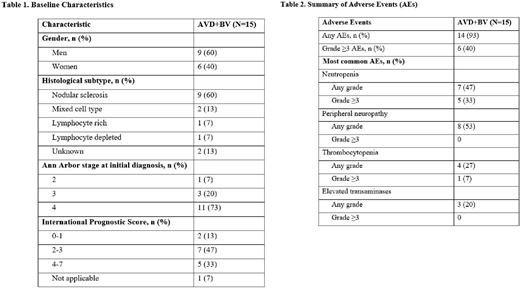
Results: A total of 15 patients were included with a median age of 23 years (range 16-67); 9 (60%) patients were men. At baseline, B symptoms (fever, night sweats, and unintentional weight loss) were observed in 7 (47%) patients and bulky disease was present in 9 (60%) patients. Nodular sclerosis was the most common histological subtype found in 9 (60%) patients and the majority of patients (11; 73%) had stage IV disease (Table 1). Of the 15 patients studied, effectiveness data were available for 13 patients who completed the treatment; 2 remained on treatment till the writing of this report. The ORR achieved with AVD+BV combination therapy was 100%; CR was achieved in 10/13 (77%) and all of them remained in the state of CR after a median follow-up of 12 months. Three patients (23%) achieved PR during treatment but proceeded to second-line treatment because of either disease progression (2; 15%) or unsatisfactory response (1; 8%) by the end of treatment. In the safety analysis population, the most common adverse event (AE) of any grade was peripheral neuropathy observed in 8/15 (53.3%) patients followed by neutropenia in 7/15 (47%) patients (Table 2). Neutropenia was also the most common grade ≥3 AE observed in 5/15 (33%) patients. Lung infection of grade ≥3 was observed in one patient only.
Conclusion: Here, we reported first real-world data in China on BV plus chemotherapy (AVD) as frontline therapy in the treatment of advanced stage cHL. In consistency with the findings from clinical trials, our study results showed that the combination of AVD+BV as frontline therapy in the treatment of advanced stage II with large mass Hodgkin lymphoma was effective and safe in real-world practice.
Disclosures
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.